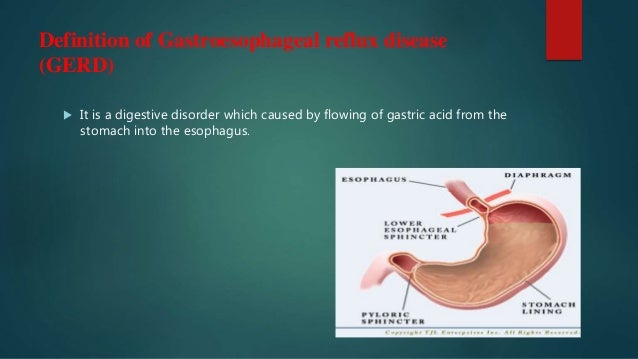
Nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs have also been implicated in the pathogenesis of gastro‐oesophageal reflux disease (gerd) 9 however, while the associations between nsaid use and peptic ulcer disease or dyspepsia are well documented, there are fewer data on the relationship between nsaids and gerd. Gerd and anti-inflammatory drugs. Nsaids including aspirin and ibuprofen can irritate the lining of the esophagus causing heartburn thus increasing the severity of gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd) or contributing to its development non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (nsaids) are pain relievers available in both over-the-counter (otc) and prescription form.
gerd and anti-inflammatory drugs
Certain medications and dietary supplements can irritate the lining of your esophagus, causing heartburn pain others can increase the severity of gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd) gerd is a chronic condition in which stomach acid flows back (refluxes) into your esophagus this backwash of acid causes irritation and inflammation of the. Learn how nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (nsaids) prescribed for inflammatory arthritis, tendinitis, and bursitis can cause ulcers. examples of nsaids include aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, and indomethacin. barrett's esophagus source: medicinenet. barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd).. In addition, it is important to review the us food and drug administration-approved indications for ppis: peptic ulcer disease, eradication of helicobacter pylori, gerd, zollinger ellison syndrome, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-associated ulcer prevention. if a patient on a long-standing ppi no longer meets an indication or wants to.